Acceptance Quality Limit (AQL) is a statistical measure used to ensure the quality of products during the manufacturing process. It is widely used in various industries to ensure that the products produced meet the required standards and specifications. AQL sets a maximum number of defects that can be accepted in a given sample size. Any more than this amount would indicate a problem with the process that needs to be resolved.
AQL works by defining the acceptable number of manufacturing defects in a sample size that will be allowed to pass through the quality testing process. The sample size is selected randomly, and the number of defects allowed is determined based on the specific AQL level that has been set. For example, if the AQL level is set at 1%, then a sample size of 100 would allow only one defective product to be accepted. Any more than one defective product in the sample size would indicate a problem with the manufacturing process.
AQL can be applied to a wide range of products, from electronic equipment to food products. In the electronic industry, AQL is used to identify and control the number of defects in electronic components that can lead to system failure. In the food industry, AQL is used to ensure that the food products meet the required standards and that there are no contaminants or harmful substances present.

Importance of AQL in Controlling Production Quality
The acceptance quality limit (AQL) is a fundamental concept used in quality control processes to ensure that goods produced meet the desired quality standards. AQL sets a measurable standard for determining the maximum number of defects allowed in any given sample size.
AQL is extremely important in controlling production quality as it helps to identify defects or imperfections in products that can negatively affect consumer satisfaction. By setting a maximum allowable defect threshold, manufacturers can control the quality of their products, reduce the potential for recalls, and minimize the overall cost of production.
For example, in the textile industry, AQL is used to determine the level of defects allowed in clothing items. If the allowable defect rate is exceeded, the manufacturer can identify the weak link in the production and rectify the issue before an entire batch of faulty garments is produced. In the food industry, AQL is used to prevent food contamination and reduce the risk of illness or injury to consumers.
Without AQL, manufacturers would have no standard for measuring quality. Instead, products would be subject to subjective assessments of quality, which would result in inconsistencies and poor-quality products.
The AQL is calculated using a combination of factors such as the sample size, the level of quality desired, and other variables such as the complexity of the production process. By setting a quantifiable standard for quality, it becomes easier for manufacturers to make informed decisions and take corrective actions when necessary.

The Process to Determine AQL Level for Product
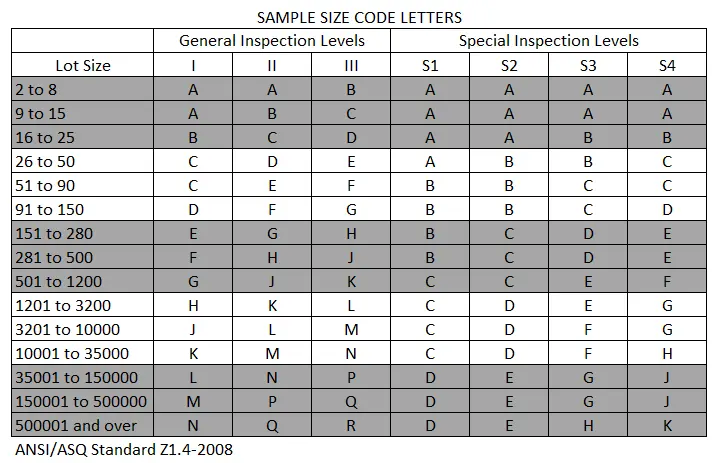
The process to determine the AQL level for a product involves different steps. The first step is to identify the purpose of the product and what quality level is expected by the consumer. The next step is to identify the inspection level, which is the number of units that need to be inspected to ensure that the product meets the quality expectations. The inspection level is determined by the size of the production run, the cost of testing, and the level of risk the consumer is willing to accept.
Once the inspection level has been determined, the next step is to establish an acceptable quality level (AQL). This is the maximum number of defects that are acceptable in the sample inspected. The AQL level is typically determined by the manufacturer or retailer but is often guided by industry standards or government regulations.
Once the AQL level has been established, the sample size is selected for inspection. The sample size is determined by statistical methods, and the number of units to be tested depends on the inspection level and the AQL level. The sample size can vary depending on the type of product, the production process, and the quality level required.
During the inspection process, each unit in the sample is evaluated to determine whether it meets the quality criteria established by the AQL level. Defective units are counted and recorded, and if the number of defects exceeds the AQL level, then the entire production run may be rejected, and corrective action must be taken to address the quality issue.
It is important to note that the AQL level is not the same as the defect rate. The defect rate is the actual percentage of defects in the production run, while the AQL level sets the maximum number of defects that are acceptable. This means that a production run may have a defect rate below the AQL level but still be rejected if the number of defects found in the sample exceeds the AQL level.

Examples of How AQL Can Be Used in Different Types of Goods
By setting a maximum number of defects that can be accepted in a given sample size, AQL helps identify potential problems in the production process before they become larger issues. Let’s take a closer look at how AQL can be applied to different types of goods.
1. Clothing
Clothing is one of the most common products that require quality control, as consumers often have high expectations for fit, comfort, and appearance. For example, AQL can be used to ensure that the stitching on a shirt or pair of pants is strong enough to hold up over time, or that the fabric is free from stains or defects.
A clothing manufacturer might test a sample size of 50 garments using an AQL of 2.5%, which would allow for no more than 1 or 2 defects in the sample. If more than 2 garments in the sample have defects, the manufacturer knows that there is likely an issue with the production process that needs to be addressed.
2. Electronics
Electronic devices such as smartphones, laptops, and televisions require careful quality control to ensure that they function properly and meet safety standards. AQL can be used to test various components of these devices, such as the screen, battery, or charging port.
For example, a smartphone manufacturer might test a sample size of 100 phones using an AQL of 1.0%, which would allow for no more than 1 defect in the sample. If a defect is found, such as a cracked screen or malfunctioning button, the manufacturer can investigate the cause and take steps to prevent it from happening in future batches.
3. Food and Beverages
Food and beverages must meet strict safety and quality standards to avoid potential health risks for consumers. AQL can be used to test for contaminants, bacterial growth, or other issues that could affect the safety and quality of the product.
For example, a soft drink bottler might test a sample size of 500 bottles using an AQL of 0.5%, which would allow for no more than 2 defects in the sample. If more than 2 bottles are found to have defects, such as broken seals or contaminated liquid, the bottler can investigate the source of the problem and take corrective action.

Strategies for Implementing AQL Standards in Production Processes
Implementing AQL standards in the production process can be a daunting task. Therefore, this article will explore key strategies for implementing AQL standards in production processes.
1. Develop a comprehensive quality control plan
Before implementing AQL standards, it’s important to create a comprehensive quality control plan. This plan should identify the critical points in the production process where defects are most likely to occur. It should also establish clear standards for identifying, reporting, and correcting those defects. A comprehensive quality control plan will help ensure that AQL standards are effectively implemented and consistently followed.
2. Establish effective communication channels
Effective communication is essential when it comes to implementing AQL standards. All stakeholders in the production process should be informed about the importance of AQL standards and their role in maintaining product quality. It’s important to create a culture of quality that emphasizes the importance of meeting and exceeding AQL standards. Clear communication channels must be established to ensure that information flows seamlessly among all stakeholders.
3. Train employees on AQL standards
To successfully implement AQL standards, it’s essential to train all employees involved in the production process. This training should focus on the importance of AQL standards and how they contribute to overall product quality. Employees should also be trained on how to identify defects, report them, and take corrective actions. This training should be ongoing, and all employees should be regularly retrained and updated on any changes to AQL standards.
4. Conduct regular inspections and audits
Regular inspections and audits can help identify and correct problems with the production process before they escalate. These inspections should be conducted regularly, and the results should be tracked and reported. Any issues identified during inspections should be addressed immediately to prevent further defects from occurring.
5. Use technology and automation
Technology and automation can help ensure that AQL standards are consistently met. For example, automated inspection systems can quickly and accurately check for defects, reducing the time and cost associated with manual inspections. Additionally, real-time monitoring systems can identify and flag any deviations from AQL standards, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, AQL is an efficient method of ensuring product quality and customer satisfaction. It helps manufacturers to define quality characteristics, create benchmarks, and set specific parameters to achieve these standards. It is a vital tool that ensures the final product meets the expected quality level, ensuring customer satisfaction, loyalty, and retention.